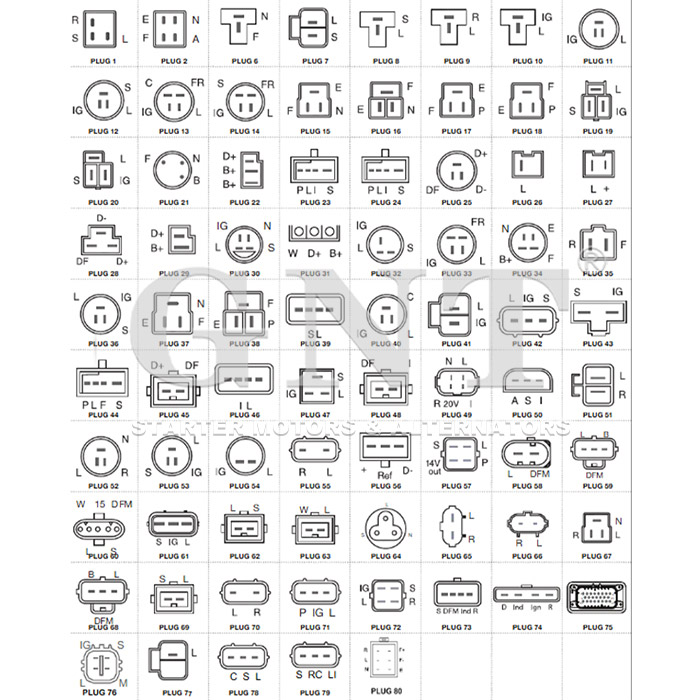
Introduction
A gear-reduction starter refers to a starter motor equipped with a gear reducer between the armature shaft and the drive gear.
Details
Working Principle
The power output (P) of a series-wound DC motor is directly proportional to both its torque (T) and rotational speed (n), expressed as P ∝ T × n. This principle demonstrates that maintaining constant power while increasing motor speed and decreasing torque can significantly reduce the starter's size and weight. However, the reduced torque output from high-speed, low-torque motors cannot meet engine starting requirements. Therefore, installing a gear reducer between the motor's armature shaft and drive gear effectively decreases output speed while increasing torque.
Three Types of Gear-Reduction Starters
External Gear Reduction Starter
Features an idler gear between armature shaft and drive gear
The solenoid core is coaxial with the drive gear, enabling direct engagement without a shift fork
Distinctive external appearance compared to conventional starters
Larger center distance limits maximum reduction ratio (typically ≤5:1)
Primarily used in low-power applications
Internal Gear Reduction Starter
Compact center distance allows higher reduction ratios
Requires conventional shift fork mechanism for gear engagement
Similar external appearance to standard starters
Generates higher operational noise
Suitable for higher-power applications
Planetary Gear Reduction Starter
Extremely compact design with high reduction ratios
Exceptional mechanical efficiency (typically 92-95%)
Coaxial input/output shafts eliminate radial loads on armature
Minimal vibration due to balanced load distribution
Enables significant size and weight reduction
Permanent Magnet (PM) Starters
PM starters utilize permanent magnet materials for field excitation, eliminating traditional field windings and iron cores. This innovation:
Simplifies overall structure
Reduces size and weight by 40-50%
Enhances reliability
Conserves metal materials
Improves energy efficiency
PM Gear-Reduction Starters
These advanced starters combine permanent magnet motors with gear reducers, offering:
Further reductions in size and weight
Higher torque density (28-35 Nm/kg)
Lower power consumption
Widespread adoption in modern vehicles
Particularly suitable for start-stop systems and hybrid vehicles
Technical Advantages:
30-50% weight reduction compared to conventional starters
20-30% lower current draw during cold cranking
Improved cold-weather performance
Longer service life (typically 100,000+ start cycles)
Maintenance Considerations
Planetary gear sets require special high-temperature grease (MIL-PRF-81322 grade)
Regular inspection of sun gear splines recommended every 50,000 cycles
Magnet assemblies sensitive to thermal shock and vibration



 0
0 May, 29, 2022
May, 29, 2022